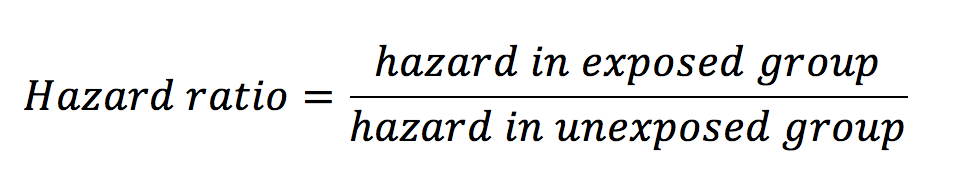Hazard Ratio Formula Example
How to calculate the hazard ratio of two groups survival timesThanks for watching. For example the risk ratio of 5 reveals a 5.
The segment of the risk ratio above or below 1 quantifies the relative increase ordecrease in risk associated with exposure.

Hazard ratio formula example. It may be different at different times of follow up. WHEN THE INCREASE IN THE CATEGORY VARIABLE X C-X A DOES NOT EQUAL TO 1 UNIT. Response rate median survival Comparative Trials.
In the Cox-model this can be shown to translate to the following relationship between group survival functions. For example a hazard ratio of 2 is thought to mean that a group has twice the chance of dying than a comparison group. It uses information collected at different times.
Where r is the hazard ratio. For example if T denote the age of death then the hazard function ht is expected to be decreasing at rst and then gradually increasing in the end re ecting higher hazard of infants and elderly. ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 412502 03 67 66 Hazard ratio HR Broadly equivalent to relative risk RR.
For example if we have the two-sided 90 interval with hazard ratio limits 25 10 we can actually say that hazard ratios less than 25 are excluded with 95 confidence precisely because a 90 two-sided interval is nothing more than two conjoined 95 one-sided intervals. Hazard Change of Variables Discrete RV Previously we have discussed changes of variables functions of random variables in terms of the e ect on things like expectation and variance. 1t 0t e e is referred to as the hazard ratio HR or relative risk RR is the log hazard ratio or log relative risk.
This is how you can interpret and report it. A hazard ratio of exactly 10 means that the study drug provides zero risk reduction compared to the control treatment. For example 102 5 which is the.
The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35 compared to the group of high-calorie diet. Vapor Hazard Ratio Example Benzene VP 952 mmHg and OEL of 05 ppm Vapor Hazard Ratio Benzene 1904 MEK VP 867 mmHg and OEL of 200 PPM Vapor Hazard Ratio of 042 Toulene VP 284 mmHg and OEL of 20 PPM Vapor Hazard Ratio of 142 What are the Ventilation Requirements for each substance. For example let Xbe a random variable with a pmf given by fx then let Y be a random variable that is a linear transform of X such that Y aXb then EY E.
The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a high-calorie diet. The risk ratio of 499 about 5 indicates that risk in the exposed group is 5-times that of thenon-exposed group. Applying formula 1 eβˆ hazard ratio ˆ eβ X X B A eβˆ 1 0 eβˆ The hazard ratio in the above SAS output means that the hazard of death in treatment group B is 0550 times the hazard of death in treatment group A.
Since the hazard is a function of time the hazard ratio say for exposed versus unexposed is also a function of time. If you had just one number to summarize the inference from your study. The numerical value can be a fraction of 10 or it can be greater than 10.
λ t λ 0. The hazard ratio must be 1 and the lower limit of the 95 confidence interval of the hazard ratio must be 1 which was the case in this example. For example if the hazard is 02 at time t and the time units are months then on average 02 events are expected per person at risk per month.
The hazard function may assume more a complex form. For example if the. Lets say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065.
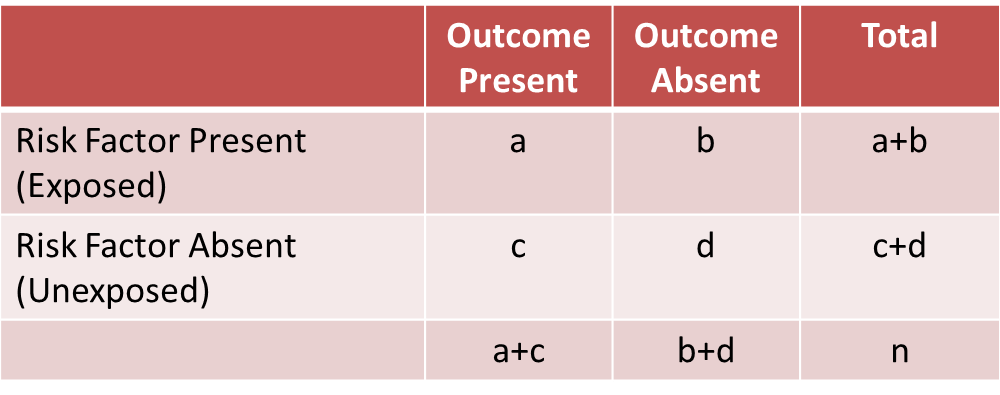
The hazard ratio is a clinical trial statistic that allows the physician to say with confidence that healing is faster with the new drug. In an outbreak of tuberculosis among prison inmates in South Carolina in 1999 28 of 157 inmates residing on the East wing of the dormitory developed tuberculosis compared with 4 of 137 inmates residing on the West wing These data are summarized in the two-by-two table so called because it has two rows for the exposure and two columns for the. Odds ratio hazard ratio.
A hazard ratio of 3 means that three times the number of events are seen in the treatment group at any point in time. MTD maximum tolerable dose Safety and Efficacy Trials. Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5.
Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time. Therefore with a hazard ratio of 2 if. This implies that the ratio of the two hazards is a constant e which does NOT depend on time t.
Another interpretation is based on the reciprocal of the hazard. In other words the hazards of the two groups remain proportional over time. In another study of smoking and lung cancer the lung cancer mortality rate among nonsmokers was 007 per 1000 persons per year The lung cancer mortality rate among persons who smoked 114 cigarettes per day was 057 lung cancer deaths per 1000 persons per yearCalculate the attributable proportion.
For example a hazard ratio of 070 means that the study drug provides 30 risk reduction compared to the control treatment 25. Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities. 100 400100 400 increase in risk with exposure.
As a formula the hazard ratio which can be defined as the relative risk of an event happening at time t is. A point estimate is a one- number summary of data.

On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value

Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
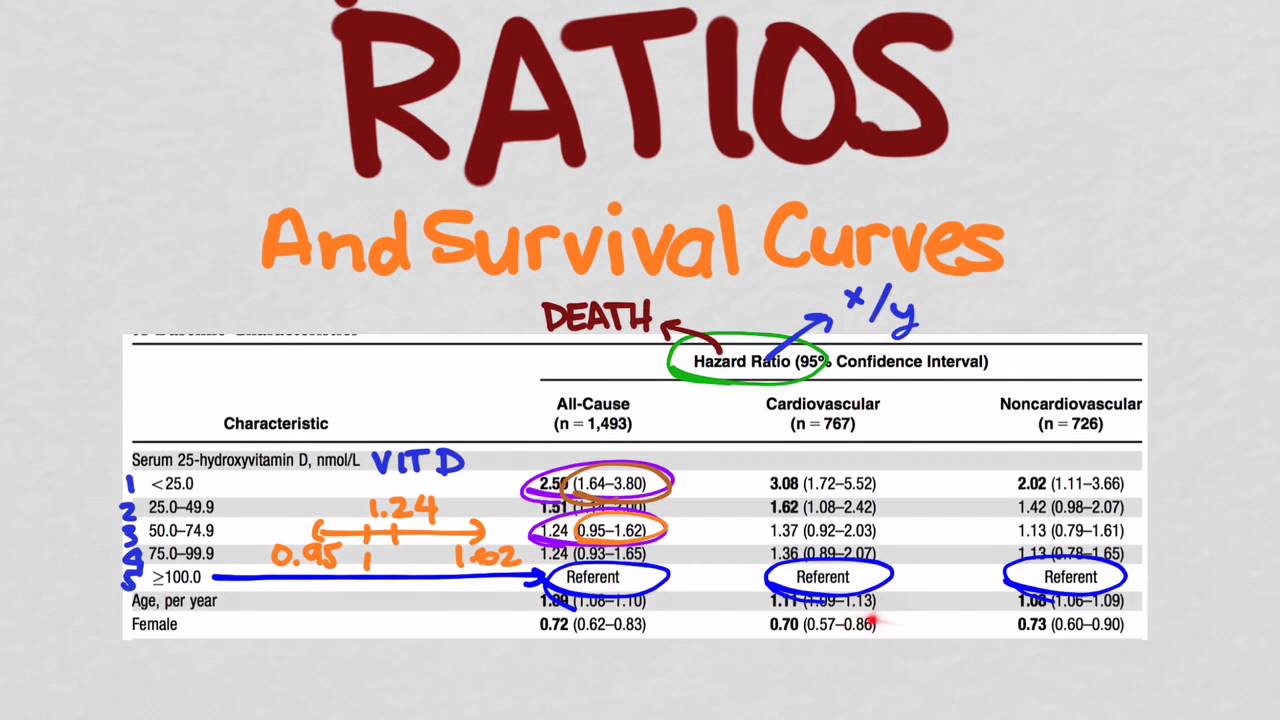
Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube

On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value
Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value

Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube

Calculating Hazard Ratios Survival Analysis Youtube

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor

How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube

Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value

Stepwise Cox Regression Analysis In Spss Dessai S Simha V Patil V Cancer Res Stat Treat

How To Calculate Relative Risk Reduction Youtube
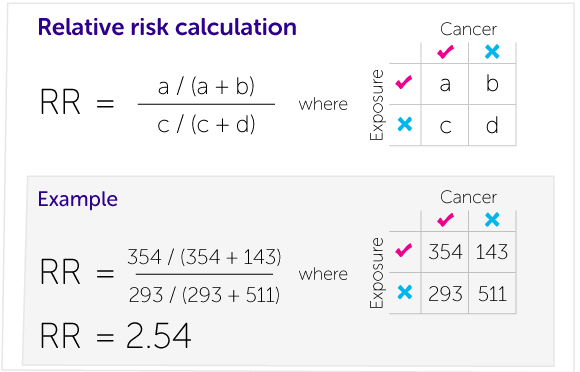
Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk

In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or
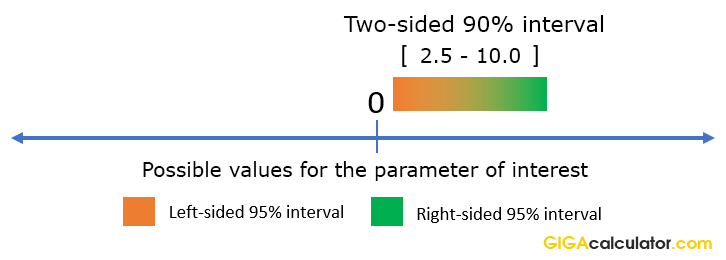
Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value

Coxs Proportional Hazards Regression Model Principles

Lecture 12 Cox Proportional Hazards Model Ppt Video Online Download